What is a Turbocharger (Turbine)?
Turbocharger – is a forced induction system used in internal combustion engines to increase their efficiency and power. The main function of a turbocharger is to increase the amount of air entering the engine, allowing more fuel to be burned and extracting more power from the same engine volume.
Turbochargers are used not only in cars but also in trucks, ships, airplanes, and industrial machinery. Their application allows achieving a higher power-to-weight ratio, reducing fuel consumption and emissions, which is particularly important for modern environmental requirements.
How Does a Turbocharger Work?
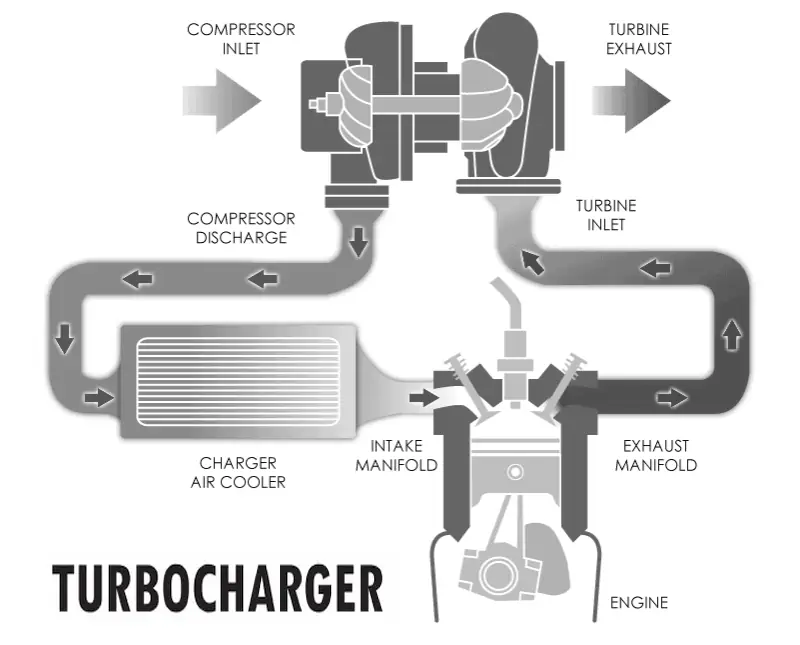
A turbocharger consists of two main components: the turbine and the compressor, which are connected by a common shaft.
- The turbine is connected to the exhaust system and is driven by the flow of exhaust gases. This allows the utilization of otherwise wasted energy.
- The compressor is connected to the air intake system and increases the pressure of the air entering the engine.
When the engine is running, the exhaust gases flow through the turbine wheel, spinning the shaft, which in turn drives the compressor wheel. The compressor compresses the intake air, and the compressed air enters the engine through the intercooler (intercooler), which reduces the air temperature and increases its density, improving combustion efficiency.
Why is a Turbocharger Needed?
A turbocharger is used to address several important issues in internal combustion engines:
- Increased engine power – compressed air allows more fuel to be burned, extracting more power without the need to increase engine displacement.
- Better utilization of exhaust gas energy – the turbine uses exhaust gases that would otherwise be wasted.
- Reduced fuel consumption – turbocharged engines achieve higher efficiency, extracting more power from less fuel.
- Reduced emissions – due to more efficient combustion, the amount of pollutants emitted can be lower, making turbo engines more environmentally friendly.
History and Invention of Turbochargers
The first principles of the turbocharger were described in 1905 by Swiss engineer Alfred Büchi. He patented the idea of using exhaust gas energy to compress air in internal combustion engines. However, the first practical turbochargers were only introduced in the 1920s.
In aviation, turbochargers became a significant innovation during World War II – they allowed fighter planes to fly at high altitudes, where conventional engines would lose power due to lower atmospheric pressure. In the automotive industry, turbochargers became widely used in the 1970s, especially with the development of diesel engines.
Where are Turbochargers Used?
Although turbochargers are most commonly associated with passenger cars, their application is much broader:
- Automotive industry – used in both gasoline and diesel engines to increase power and efficiency.
- Trucks – help reduce fuel consumption and provide greater traction.
- Aviation – fighter jets and passenger planes use turbochargers to operate efficiently at low atmospheric pressure.
- Industry – turbochargers are used in gas turbines, power generators, and ships to make better use of fuel.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Like any mechanism, turbochargers have both advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- High power from a small displacement – allows achieving a high power-to-weight ratio.
- Better fuel efficiency – reduces fuel consumption compared to naturally aspirated engines.
- Ecology – lower CO₂ and other pollutant emissions.
Disadvantages
- Turbo lag – the time it takes for the turbo to reach optimal pressure.
- More complex maintenance – requires regular oil changes and high-quality filters.
- High operating temperature – can cause failures if cooling is insufficient.
The turbocharger is an essential component of modern internal combustion engines, allowing more efficient fuel use and reducing environmental pollution. Although it has some disadvantages, ongoing improvements in technology are helping to minimize these issues and enhance system performance. In the future, we can expect even more efficient turbochargers with advanced control systems, further improving their operation.